Performance
SRS提供了一系列工具来定位性能瓶颈和内存泄漏,这些在./configure && make后的summary中是有给出来用法的,不过不是很方便,所以特地把用法写到这个文章中。
文中所有的工具,对于其他的linux程序也是有用的。
Note: 所有工具用起来都会导致SRS性能低下,所以除非是排查问题,否则不要开启这些选项。
RTC
RTC是UDP的协议,先设置网卡队列缓冲区,下面命令是UDP分析常用的:
# 查看UDP缓冲区长度,默认只有200KB左右。
sysctl net.core.rmem_max
sysctl net.core.rmem_default
sysctl net.core.wmem_max
sysctl net.core.wmem_default
# 修改缓冲区长度为16MB
sysctl net.core.rmem_max=16777216
sysctl net.core.rmem_default=16777216
sysctl net.core.wmem_max=16777216
sysctl net.core.wmem_default=16777216
Note: 对于Docker,在宿主机上设置后容器就自然生效了,注意需要先设置参数然后再启动容器(或者启动容器中的SRS进程),也就是Docker容器启动进程时读取的是宿主机的这个内核配置。
Note:如果希望在Docker中设置这些参数,只能以
--network=host方式启动,也就是复用宿主机的网络。注意如果不需要在Docker中设置是不依赖这种方式的。
也可以修改系统文件/etc/sysctl.conf,重启也会生效:
# vi /etc/sysctl.conf
# For RTC
net.core.rmem_max=16777216
net.core.rmem_default=16777216
net.core.wmem_max=16777216
net.core.wmem_default=16777216
查看接收和发送的丢包信息:
# 查看丢包
netstat -suna
# 查看30秒的丢包差
netstat -suna && sleep 30 && netstat -suna
实例说明:
224911319 packets received,这是接收到的总包数。65731106 receive buffer errors,接收的丢包,来不及处理就丢了。123534411 packets sent,这是发送的总包数。0 send buffer errors,这是发送的丢包。
Note: SRS的日志会打出UDP接收丢包和发送丢包,例如
loss=(r:49,s:0),意思是每秒有49个包来不及收,发送没有丢包。
Note:注意Docker虽然读取了宿主机的内核网络参数,但是
netstat -su获取的数据是和宿主机是不同的,也就是容器的丢包得在容器中执行命令获取。
查看接收和发送的长度:
netstat -lpun
实例说明:
Recv-Q 427008,程序的接收队列中的包数。Established: The count of bytes not copied by the user program connected to this socket.Send-Q 0,程序的发送队列中的包数目。Established: The count of bytes not acknowledged by the remote host.
下面是netstat的一些参数:
--udp|-u筛选UDP协议。--numeric|-n显示数字IP或端口,而不是别名,比如http的数字是80.--statistics|-s显示网卡的统计信息。--all|-a显示所有侦听和非侦听的。--listening|-l只显示侦听的socket。--program|-p显示程序名称,谁在用这个FD。
PERF
PERF是Linux性能分析工具。
可以实时看到当前的SRS热点函数:
perf top -p $(pidof srs)
或者记录一定时间的数据:
perf record -p $(pidof srs)
# 需要按CTRL+C取消record,然后执行下面的
perf report
记录堆栈,显示调用图:
perf record -a --call-graph fp -p $(pidof srs)
perf report --call-graph --stdio
Note: 也可以打印到文件
perf report --call-graph --stdio >t.txt。
Remark: 由于ST的堆栈是不正常的,perf开启
-g后记录的堆栈都是错乱的,所以perf只能看SRS的热点,不能看堆栈信息;如果需要看堆栈,请使用GPERF: GCP,参考下面的章节。
ASAN
Asan 就是 Google Address Sanitizer.
ASAN: Usage
SRS5+内置和默认支持ASAN,检测内存泄露、野指针和越界等问题。
若你的系统不支持ASAN,可以编译时关闭,相关选项如下:
./configure -h |grep asan
--sanitizer=on|off Whether build SRS with address sanitizer(asan). Default: on
--sanitizer-static=on|off Whether build SRS with static libasan(asan). Default: off
--sanitizer-log=on|off Whether hijack the log for libasan(asan). Default: off
开启内存泄露检测,参考halt_on_error 和 detect_leaks 的详细说明:
ASAN_OPTIONS=halt_on_error=1:detect_leaks=1 ./objs/srs -c conf/console.conf
ASAN检查内存问题很准确,推荐开启。
ASAN: Preload
如果你遇到下面的错误:
==4181651==ASan runtime does not come first in initial library list; you should either link runtime
to your application or manually preload it with LD_PRELOAD.
你应该preload ASAN库:
LD_PRELOAD=$(find /usr -name libasan.so.5 2>/dev/null) ./objs/srs -c conf/console.conf
Note: 一般而言,libasan.so 的路径是
/usr/lib64/libasan.so.5
ASAN: Options
默认情况下,SRS使用以下ASAN选项:
extern "C" const char *__asan_default_options() {
return "halt_on_error=0:detect_leaks=0:alloc_dealloc_mismatch=0";
}
halt_on_error=0: 出现错误时不会退出,只是打印消息,注意fatal错误还是会退出,参考 halt_on_error.detect_leaks=0: 禁用内存泄露的检测,由于daemon父进程会退出,全局变量会被认为是内存泄露,导致daemon启动失败,参考 detect_leaks.alloc_dealloc_mismatch=0: GDB调试程序时,可能会出现这个错误。
尽管这样,你可以覆盖这些选项,比如开启内存泄露检测等:
ASAN_OPTIONS=halt_on_error=1:detect_leaks=1:alloc_dealloc_mismatch=1 ./objs/srs -c conf/console.conf
请注意,ASAN_OPTIONS 会在 main() 函数之前加载,因此可以在 shell 中设置,但不能在 main() 函数中设置。
GPROF
GPROF是个GNU的CPU性能分析工具。参考SRS GPROF,以及GNU GPROF。
Usage:
# Build SRS with GPROF
./configure --gprof=on && make
# Start SRS with GPROF
./objs/srs -c conf/console.conf
# Or CTRL+C to stop GPROF
killall -2 srs
# To analysis result.
gprof -b ./objs/srs gmon.out
GPERF
GPERF是google tcmalloc提供的cpu和内存工具,参考GPERF。
GPERF: GCP
GCP是CPU性能分析工具,就是一般讲的��性能瓶颈,看哪个函数调用占用过多的CPU。参考GCP。
Usage:
# Build SRS with GCP
./configure --gperf=on --gcp=on && make
# Start SRS with GCP
./objs/srs -c conf/console.conf
# Or CTRL+C to stop GCP
killall -2 srs
# To analysis cpu profile
./objs/pprof --text objs/srs gperf.srs.gcp*
Note: 用法可以参考cpu-profiler。
图形化展示,在CentOS上安装dot:
yum install -y graphviz
然后生成svg图片,可以用Chrome打开:
./objs/pprof --svg ./objs/srs gperf.srs.gcp >t.svg
GPERF: GMD
GMD是GPERF提供的内存Defense工具,检测内存越界和野指针。一般在越界写入时,可能不会立刻导致破坏,而是在切换到其他线程使用被破坏的对象时才会发现破坏了,所以这种内存问题很难排查;GMD能在越界和野指针使用时直接core dump,定位在那个出问题的地方。参考GMD。
Usage:
# Build SRS with GMD.
./configure --gperf=on --gmd=on && make
# Start SRS with GMD.
env TCMALLOC_PAGE_FENCE=1 ./objs/srs -c conf/console.conf
Note: 用法可以参考heap-defense。
Note: 注意GMD需要链接
libtcmalloc_debug.a,并且开启环境变量TCMALLOC_PAGE_FENCE。
GPERF: GMC
GMC是内存泄漏检测工具,参考GMC。
Usage:
# Build SRS with GMC
./configure --gperf=on --gmc=on && make
# Start SRS with GMC
env PPROF_PATH=./objs/pprof HEAPCHECK=normal ./objs/srs -c conf/console.conf 2>gmc.log
# Or CTRL+C to stop gmc
killall -2 srs
# To analysis memory leak
cat gmc.log
Note: 用法可以参考heap-checker。
GPERF: GMP
GMP是内存性能分析工具,譬如检测是否有频繁的申请和释放堆内存导致的性能问题。参考GMP。
Usage:
# Build SRS with GMP
./configure --gperf=on --gmp=on && make
# Start SRS with GMP
./objs/srs -c conf/console.conf
# Or CTRL+C to stop gmp
killall -2 srs
# To analysis memory profile
./objs/pprof --text objs/srs gperf.srs.gmp*
Note: 用法可以参考heap-profiler。
VALGRIND
VALGRIND是大名鼎鼎的内存分析工具,SRS3之后支持了。
Valgrind: Memcheck
SRS3之前,因为使用了ST,需要给ST打PATCH才能用。
valgrind --leak-check=full --show-leak-kinds=all ./objs/srs -c conf/console.conf
Remark: SRS3之前的版本,可以手动给ST打PATCH支持VALGRIND,参考state-threads,详细的信息可以参考ST#2。
Remark: SRS需要升级到对应版本,才能支持HTTP valgrind API,具体参考 #4150。
Valgrind: Incremental Memory Leak Detection
使用valgrind�检测SRS内存泄露时,尽管在ST中支持了valgrind的hook,还是有大量的误报信息。比较合理的是让valgrind报告增量的内存泄露, 这样可以避开全局和静态变量,也可以不用退出程序就可以实现检测。操作步骤如下:
- 编译SRS支持valgrind:
./configure --valgrind=on && make - 启动SRS,开启内存泄露的检测:
valgrind --leak-check=full --show-leak-kinds=all ./objs/srs -c conf/console.conf - 触发内存检测,使用curl访问API,形成校准的数据,依然有大量误报,但可以忽略这些数据:
curl http://127.0.0.1:1985/api/v1/valgrind?check=added - 多尝试几次内存检测,直到没有新增的泄露,包括possibly和reachable。
- 压测,或者针对怀疑泄露的功能测试,比如RTMP推流:
ffmpeg -re -i doc/source.flv -c copy -f flv rtmp://127.0.0.1/live/livestream - 停止推流,等待SRS清理Source内存,大概等待30秒左右。
- 增量内存泄露检测,此时报告的泄露情况就非常准确了:
curl http://127.0.0.1:1985/api/v1/valgrind?check=added
HTTP #0 11.176.19.95:42162 GET http://9.134.74.169:1985/api/v1/valgrind?check=added, content-length=-1
query check=added
==1481822== LEAK SUMMARY:
==1481822== definitely lost: 0 (+0) bytes in 0 (+0) blocks
==1481822== indirectly lost: 0 (+0) bytes in 0 (+0) blocks
==1481822== possibly lost: 3,406,847 (+0) bytes in 138 (+0) blocks
==1481822== still reachable: 18,591,709 (+0) bytes in 819 (+0) blocks
==1481822== of which reachable via heuristic:
==1481822== multipleinheritance: 536 (+0) bytes in 4 (+0) blocks
==1481822== suppressed: 0 (+0) bytes in 0 (+0) blocks
==1481822== Reachable blocks (those to which a pointer was found) are not shown.
Note: 为了避免HTTP请求本身对valgrind的干扰,SRS使用单独的coroutine定时检查,因此访问API后,可能需要等待几秒才会触发检测。
Valgrind: Still Reachable
有时候,你会收到很多still reachable的报告,这是因为静态或全局变量,比如这个例子:
==3430715== 1,040 (+1,040) bytes in 1 (+1) blocks are still reachable in new loss record 797 of 836
==3430715== at 0x4C3F963: calloc (vg_replace_malloc.c:1595)
==3430715== by 0x7D8DB0: SrsConfig::get_hls_vcodec(std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, std::allocator<char> >) (srs_app_config.cpp:7156)
==3430715== by 0x781283: SrsHlsMuxer::segment_open() (srs_app_hls.cpp:418)
# It's caused by static variable:
string SrsConfig::get_hls_vcodec(string vhost) {
SRS_STATIC string DEFAULT = "h264";
SrsConfDirective* conf = get_hls(vhost);
if (!conf) {
return DEFAULT;
你可以调整下测试步骤,在触发内存检测前,先推流来初始化这些静态和全局变量,然后再次推流和内存增量泄露的检测:
- 启动SRS后先推流,初始化静态和全局变量,然后停止推流:
ffmpeg -re -i doc/source.flv -c copy -f flv rtmp://127.0.0.1/live/livestream - 触发内存检测,使用curl访问API,形成校准的数据,依然有大量误报,但可以忽略这些数据:
curl http://127.0.0.1:1985/api/v1/valgrind?check=added - 多尝试几次内存检测,直到没有新增的泄露,包括possibly和reachable。
- 压测,或者针对怀疑泄露的功能测试,比如RTMP推流:
ffmpeg -re -i doc/source.flv -c copy -f flv rtmp://127.0.0.1/live/livestream - 停止推流,等待SRS清理Source内存,大概等待30秒左右。
- 增量内存泄露检测,此时报告�的泄露情况就非常准确了:
curl http://127.0.0.1:1985/api/v1/valgrind?check=added
由于变量已经初始化了,所以still reachable的干扰报告就不会有了。
Syscall
系统调用的性能排查,参考strace -c -p PID
OSX
在OSX/Darwin/Mac系统,可以用Instruments,在xcode中选择Open Develop Tools,就可以看到Instruments,也可以直接找这个程序,参考Profiling c++ on mac os x
instruments -l 30000 -t Time\ Profiler -p 72030
Remark: 也可以在Active Monitor中选择进程,然后选择Sample采样。
Multiple Process and Softirq
多核时,一般网卡软中断(内核网络传输)在CPU0上,可以把SRS调度到其他CPU:
taskset -p 0xfe $(pidof srs)
或者,指定SRS运行在CPU1上:
taskset -pc 1 $(pidof srs)
调整后,可以运行top,然后按数字1,可以看到每个CPU的负载:
top # 进入界面后按数字1
#%Cpu0 : 1.8 us, 1.1 sy, 0.0 ni, 90.8 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 6.2 si, 0.0 st
#%Cpu1 : 67.6 us, 17.6 sy, 0.0 ni, 14.9 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st
或者使用mpstat -P ALL
mpstat -P ALL
#01:23:14 PM CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %gnice %idle
#01:23:14 PM all 33.33 0.00 8.61 0.04 0.00 3.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 55.02
#01:23:14 PM 0 2.46 0.00 1.32 0.06 0.00 6.27 0.00 0.00 0.00 89.88
#01:23:14 PM 1 61.65 0.00 15.29 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 23.03
Note: 可以使用命令
cat /proc/softirqs,查看所有CPU的具体软中断类型,参考Introduction to deferred interrupts (Softirq, Tasklets and Workqueues)。
Note: 如果将SRS强制绑定在CPU0上,则会导致较高的
softirq,这可能是进程和系统的软中断都在CPU0上,可以看到si也比分开的要高很多。
如果是多CPU,比如4CPU,则网卡中断可能会绑定到多个CPU,可以通过下面的命令,查看网卡中断的绑定情况:
# grep virtio /proc/interrupts | grep -e in -e out
29: 64580032 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge virtio0-input.0
30: 1 49 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge virtio0-output.0
31: 48663403 0 11845792 0 PCI-MSI-edge virtio0-input.1
32: 1 0 0 52 PCI-MSI-edge virtio0-output.1
# cat /proc/irq/29/smp_affinity
1 # 意思是virtio0的接收,绑定到CPU0
# cat /proc/irq/30/smp_affinity
2 # 意思是virtio0的发送,绑定到CPU1
# cat /proc/irq/31/smp_affinity
4 # 意思是virtio1的接收,绑定到CPU2
# cat /proc/irq/32/smp_affinity
8 # 意思是virtio1的发送,绑定到CPU3
我们可以强制将网卡软中断绑定到CPU0,参考Linux: scaling softirq among many CPU cores和SMP IRQ affinity:
for irq in $(grep virtio /proc/interrupts | grep -e in -e out | cut -d: -f1); do
echo 1 > /proc/irq/$irq/smp_affinity
done
Note:如果要绑定到
CPU 0-1,执行echo 3 > /proc/irq/$irq/smp_affinity
然后将SRS所有线程,绑定到CPU0之外的CPU:
taskset -a -p 0xfe $(cat objs/srs.pid)
可以看到,软中断默认分配方式占用较多CPU,将软中断集中在CPU0,降低20%左右CPU。
如果要获取极高的性能,那么可以在SRS的启动脚本中,在启动SRS之前,执行绑核和绑软中断的命令。
Process Priority
可以设置SRS为更高的优先级,可以获取更多的CPU时间:
renice -n -15 -p $(pidof srs)
Note: nice的值从
-20到19,默认是0,一般ECS的优先的进程是-10,所以这里设置为-15。
可以从ps中,看到进程的nice,也就是NI字段:
top -n1 -p $(pidof srs)
# PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
# 1505 root 5 -15 519920 421556 4376 S 66.7 5.3 4:41.12 srs
Performance Banchmark
对比SRS和高性能nginx-rtmp的Performance,SRS为单进程,nginx-rtmp支持多进程,为了对比nginx-rtmp也只开启一个进程。
提供详细的性能测试的过程,可以为其他性能测试做参考,譬如测试nginx-rtmp的多进程,和srs的forward对比之类。
最新的性能测试数据,请参考performance。
Hardware
本次对比所用到的硬件环境,使用虚拟机,客户端和服务器都运行于一台机器,避开网络瓶颈。
- 硬件: 笔记本上的虚拟机
- 系统: CentOS 6.0 x86_64 Linux 2.6.32-71.el6.x86_64
- CPU: 3 Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-3520M CPU @ 2.90GHz
- 内存: 2007MB
OS
超过1024的连接数测试需要打开linux的限制。且必须以root登录和执行。
- 设置连接数:
ulimit -HSn 10240 - 查看连接数:
[root@dev6 ~]# ulimit -n
10240
-
重启srs:
sudo /etc/init.d/srs restart -
注意:启动服务器前必须确保连接数限制打开。
NGINX-RTMP
NGINX-RTMP使用的版本信息,以及编译参数。
- NGINX: nginx-1.5.7.tar.gz
- NGINX-RTMP: nginx-rtmp-module-1.0.4.tar.gz
- 下载页面,包含编译脚本:下载nginx-rtmp
- 编译参数:
./configure --prefix=`pwd`/../_release \
--add-module=`pwd`/../nginx-rtmp-module-1.0.4 \
--with-http_ssl_module && make && make install
- 配置nginx:
_release/conf/nginx.conf
user root;
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 10240;
}
rtmp{
server{
listen 19350;
application live{
live on;
}
}
}
- 确保连接数没有限制:
[root@dev6 nginx-rtmp]# ulimit -n
10240
- 启动命令:
./_release/sbin/nginx - 确保nginx启动成功:
[root@dev6 nginx-rtmp]# netstat -anp|grep 19350
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:19350 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 6486/nginx
SRS
SRS接受RTMP流,并转发给nginx-rtmp做为对比。
SRS的版本和编译参数。
- SRS: SRS 0.9
- 编译参数:
./configure && make - 配置SRS:
conf/srs.conf
listen 1935;
max_connections 10240;
vhost __defaultVhost__ {
forward 127.0.0.1:19350;
}
- 确保连接数没有限制:
[root@dev6 trunk]# ulimit -n
10240
- 启动命令:
nohup ./objs/srs -c conf/srs.conf >/dev/null 2>&1 & - 确保srs启动成功:
[root@dev6 trunk]# netstat -anp|grep "1935 "
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:1935 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 6583/srs
Publish and Play
使用ffmpeg推送SRS的实例流到SRS,SRS转发给nginx-rtmp,可以通过vlc/srs-players观看。
推送RTMP流到服务器和观看。
- 启动FFMPEG循环推流:
for((;;)); do \
./objs/ffmpeg/bin/ffmpeg \
-re -i doc/source.flv \
-acodec copy -vcodec copy \
-f flv rtmp://127.0.0.1:1935/live/livestream; \
sleep 1;
done
- 查看服务器的地址:
192.168.2.101
[root@dev6 nginx-rtmp]# ifconfig eth0
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:8A:EC:94
inet addr:192.168.2.101 Bcast:192.168.2.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
- SRS的流地址:
rtmp://192.168.2.101:1935/live/livestream - nginx-rtmp的流地址:
rtmp://192.168.2.101:19350/live/livestream
Client
使用linux工具模拟RTMP客户端访问,参考:srs-bench
sb_rtmp_load为RTMP流负载测试工具,单个进程可以模拟1000至3000个客户端。为了避免过高负载,一个进程模拟800个客户端。
- 编译:
./configure && make - 启动参数:
./objs/sb_rtmp_load -c 800 -r <rtmp_url>
Record Data
测试前,记录SRS和nginx-rtmp的各项资源使用指标,用作对比。
- top命令:
srs_pid=$(pidof srs); \
nginx_pid=`ps aux|grep nginx|grep worker|awk '{print $2}'`; \
load_pids=`ps aux|grep objs|grep sb_rtmp_load|awk '{ORS=",";print $2}'`; \
top -p $load_pids$srs_pid,$nginx_pid
- 查看连接数命令:
srs_connections=`netstat -anp|grep srs|grep ESTABLISHED|wc -l`; \
nginx_connections=`netstat -anp|grep nginx|grep ESTABLISHED|wc -l`; \
echo "srs_connections: $srs_connections"; \
echo "nginx_connections: $nginx_connections";
- 查看服务器消耗带宽,其中,单位是bytes,需要乘以8换算成网络用的bits,设置dstat为30秒钟统计一次,数据更准:
[root@dev6 nginx-rtmp]# dstat -N lo 30
----total-cpu-usage---- -dsk/total- -net/lo- ---paging-- ---system--
usr sys idl wai hiq siq| read writ| recv send| in out | int csw
0 0 96 0 0 3| 0 0 |1860B 58k| 0 0 |2996 465
0 1 96 0 0 3| 0 0 |1800B 56k| 0 0 |2989 463
0 0 97 0 0 2| 0 0 |1500B 46k| 0 0 |2979 461
- 数据见下表:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRS | 1.0% | 3MB | 3 | 不适用 | 不适用 | 不适用 | 0.8秒 |
| nginx-rtmp | 0.7% | 8MB | 2 | 不适用 | 不适用 | 不适用 | 0.8秒 |
期望带宽(E带宽):譬如测试码率为200kbps时,若模拟1000个并发,应该是1000*200kbps=200Mbps带宽。
实际带宽(A带宽):�指服务器实际的吞吐率,服务器性能下降时(譬如性能瓶颈),可能达不到期望的带宽,会导致客户端拿不到足够的数据,也就是卡顿的现象。
客户端延迟(C延迟):粗略计算即为客户端的缓冲区长度,假设服务器端的缓冲区可以忽略不计。一般RTMP直播播放器的缓冲区设置为0.8秒,由于网络原因,或者服务器性能问题,数据未能及时发送到客户端,就会造成客户端卡(缓冲区空),网络好时将队列中的数据全部给客户端(缓冲区变大)。
srs-bench(srs-bench/sb):指模拟500客户端的srs-bench的平均CPU。一般模拟1000个客户端没有问题,若模拟1000个,则CPU简单除以2。
其中,“不适用”是指还未开始测试带宽,所以未记录数据。
其中,srs的三个连接是:
- FFMPEG推流连接。
- Forward给nginx RTMP流的一个连接。
其中,nginx-rtmp的两个连接是:
- SRS forward RTMP的一个连接。
Benchmark SRS
开始启动srs-bench模拟客户端并发测试SRS的性能。
- 启动500客户端:
./objs/sb_rtmp_load -c 500 -r rtmp://127.0.0.1:1935/live/livestream >/dev/null &
- 客户端开始播放30秒以上,并记录数据:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRS | 9.0% | 8MB | 503 | 100Mbps | 112Mbps | 12.6% | 0.8秒 |
- 再启动一个模拟500个连接的srs-bench,共1000个连接。
- 客户端开始播放30秒以上,并记录数据:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRS | 23.6% | 13MB | 1003 | 200Mbps | 239Mbps | 16.6% | 0.8秒 |
- 再启动一个模拟500个连接的srs-bench,共1500个连接。
- 客户端开始播放30秒以上,并记录数据:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRS | 38.6% | 20MB | 1503 | 300Mbps | 360Mbps | 17% | 0.8秒 |
- 再启动一个模拟500个连接的srs-bench,共2000个连接。
- 客户端开始播放30秒以上,并记录数据:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRS | 65.2% | 34MB | 2003 | 400Mbps | 480Mbps | 22% | 0.8秒 |
- 再启动一个模拟500个连接的srs-bench,共2500个连接。
- 客户端开始播放30秒以上,并记录数据:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRS | 72.9% | 38MB | 2503 | 500Mbps | 613Mbps | 24% | 0.8秒 |
由于虚拟机能力的限制,只能测试到2500并发。
Benchmark NginxRTMP
开始启动srs-bench模拟客户端并发测试SRS的性能。
- 启动500客户端:
./objs/sb_rtmp_load -c 500 -r rtmp://127.0.0.1:19350/live/livestream >/dev/null &
- 客户端开始播放30秒以上,并记录数据:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nginx-rtmp | 8.3% | 13MB | 502 | 100Mbps | 120Mbps | 16.3% | 0.8秒 |
- 再启动一个模拟500个连接的srs-bench,共1000个连接。
- 客户端开始播放30秒以上,并记录数据:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nginx-rtmp | 27.3% | 19MB | 1002 | 200Mbps | 240Mbps | 30% | 0.8秒 |
- 再启动一个模拟500个连接的srs-bench,共1500个连接。
- 客户端开始播放30秒以上,并记录数据:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nginx-rtmp | 42.3% | 25MB | 1502 | 300Mbps | 400Mbps | 31% | 0.8秒 |
- 再启动一个模拟500个连接的srs-bench,共2000个连接。
- 客户端开始播放30秒以上,并记录数据:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nginx-rtmp | 48.9% | 31MB | 2002 | 400Mbps | 520Mbps | 33% | 0.8秒 |
- 再启动一个模拟500个连接的srs-bench,共2500个连接。
- 客户端开始播放30秒以上,并记录数据:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nginx-rtmp | 74.2% | 37MB | 2502 | 500Mbps | 580Mbps | 35% | 0.8秒 |
由于虚拟机能力的限制,只能测试到2500并发。
Performance Compare
CentOS6 x86_64虚拟机,SRS和nginx-rtmp的数据对比如下:
| Server | CPU | 内存 | 连接数 | E带宽 | A带宽 | sb | C延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nginx-rtmp | 8.3% | 13MB | 502 | 100Mbps | 120Mbps | 16.3% | 0.8秒 |
| SRS | 9.0% | 8MB | 503 | 100Mbps | 112Mbps | 12.6% | 0.8秒 |
| nginx-rtmp | 27.3% | 19MB | 1002 | 200Mbps | 240Mbps | 30% | 0.8秒 |
| SRS | 23.6% | 13MB | 1003 | 200Mbps | 239Mbps | 16.6% | 0.8秒 |
| nginx-rtmp | 42.3% | 25MB | 1502 | 300Mbps | 400Mbps | 31% | 0.8秒 |
| SRS | 38.6% | 20MB | 1503 | 300Mbps | 360Mbps | 17% | 0.8秒 |
| nginx-rtmp | 48.9% | 31MB | 2002 | 400Mbps | 520Mbps | 33% | 0.8秒 |
| SRS | 65.2% | 34MB | 2003 | 400Mbps | 480Mbps | 22% | 0.8秒 |
| nginx-rtmp | 74.2% | 37MB | 2502 | 500Mbps | 580Mbps | 35% | 0.8秒 |
| SRS | 72.9% | 38MB | 2503 | 500Mbps | 613Mbps | 24% | 0.8秒 |
Performance Banchmark 4k
今天做了性能优化,默认演示流(即采集doc/source.flv文件为流)达到4k以上并发没有问题。
[winlin@dev6 srs]$ ./objs/srs -v
0.9.130
top - 19:52:35 up 1 day, 11:11, 8 users, load average: 1.20, 1.05, 0.92
Tasks: 171 total, 4 running, 167 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
Cpu0 : 26.0%us, 23.0%sy, 0.0%ni, 34.0%id, 0.3%wa, 0.0%hi, 16.7%si, 0.0%st
Cpu1 : 26.4%us, 20.4%sy, 0.0%ni, 34.1%id, 0.7%wa, 0.0%hi, 18.4%si, 0.0%st
Cpu2 : 22.5%us, 15.4%sy, 0.0%ni, 45.3%id, 1.0%wa, 0.0%hi, 15.8%si, 0.0%st
Mem: 2055440k total, 1972196k used, 83244k free, 136836k buffers
Swap: 2064376k total, 3184k used, 2061192k free, 926124k cached
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
17034 root 20 0 415m 151m 2040 R 94.4 7.6 14:29.33 ./objs/srs -c console.conf
1063 winlin 20 0 131m 68m 1336 S 17.9 3.4 54:05.77 ./objs/sb_rtmp_load -c 800 -r rtmp://127.0.0.1:1935/live/livestream
1011 winlin 20 0 132m 68m 1336 R 17.6 3.4 54:45.53 ./objs/sb_rtmp_load -c 800 -r rtmp://127.0.0.1:1935/live/livestream
18736 winlin 20 0 113m 48m 1336 S 17.6 2.4 1:37.96 ./objs/sb_rtmp_load -c 800 -r rtmp://127.0.0.1:1935/live/livestream
1051 winlin 20 0 131m 68m 1336 S 16.9 3.4 53:25.04 ./objs/sb_rtmp_load -c 800 -r rtmp://127.0.0.1:1935/live/livestream
18739 winlin 20 0 104m 39m 1336 R 15.6 2.0 1:25.71 ./objs/sb_rtmp_load -c 800 -r rtmp://127.0.0.1:1935/live/livestream
[winlin@dev6 ~]$ dstat -N lo 30
----total-cpu-usage---- -dsk/total- ---net/lo-- ---paging-- ---system--
usr sys idl wai hiq siq| read writ| recv send| in out | int csw
3 2 92 0 0 3| 11k 27k| 0 0 | 1B 26B|3085 443
32 17 33 0 0 17| 273B 60k| 69M 69M| 0 0 |4878 6652
34 18 32 0 0 16| 0 38k| 89M 89M| 0 0 |4591 6102
35 19 30 0 0 17| 137B 41k| 91M 91M| 0 0 |4682 6064
33 17 33 0 0 17| 0 31k| 55M 55M| 0 0 |4920 7785
33 18 31 0 0 17|2867B 34k| 90M 90M| 0 0 |4742 6530
32 18 33 0 0 17| 0 31k| 66M 66M| 0 0 |4922 7666
33 17 32 0 0 17| 137B 39k| 65M 65M| 0 0 |4841 7299
35 18 30 0 0 17| 0 28k| 100M 100M| 0 0 |4754 6752
32 17 33 0 0 18| 0 41k| 44M 44M| 0 0 |5130 8251
34 18 32 0 0 16| 0 30k| 104M 104M| 0 0 |4456 5718
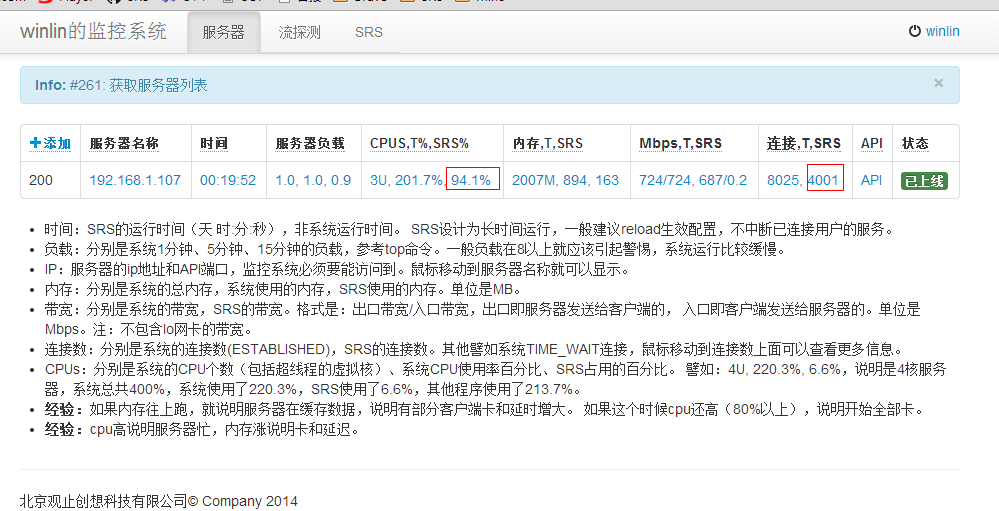
不过我是在虚拟机测试,物理机的实际情况还有待数据观察。
Performance Banchmark 6k
SRS2.0.15(注意是SRS2.0,而不是SRS1.0)支持6k客户端,522kbps的流可以跑到近4Gbps带宽,单进程。参考:https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/194
Performance Banchmark 7.5k
SRS2.0.30支持7.5k客户端,参考:https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/217
Winlin 2014.2
